TEAM Project » News » OTTOMAN TULIP ERA ARCHITECTURE

OTTOMAN TULIP ERA ARCHITECTURE
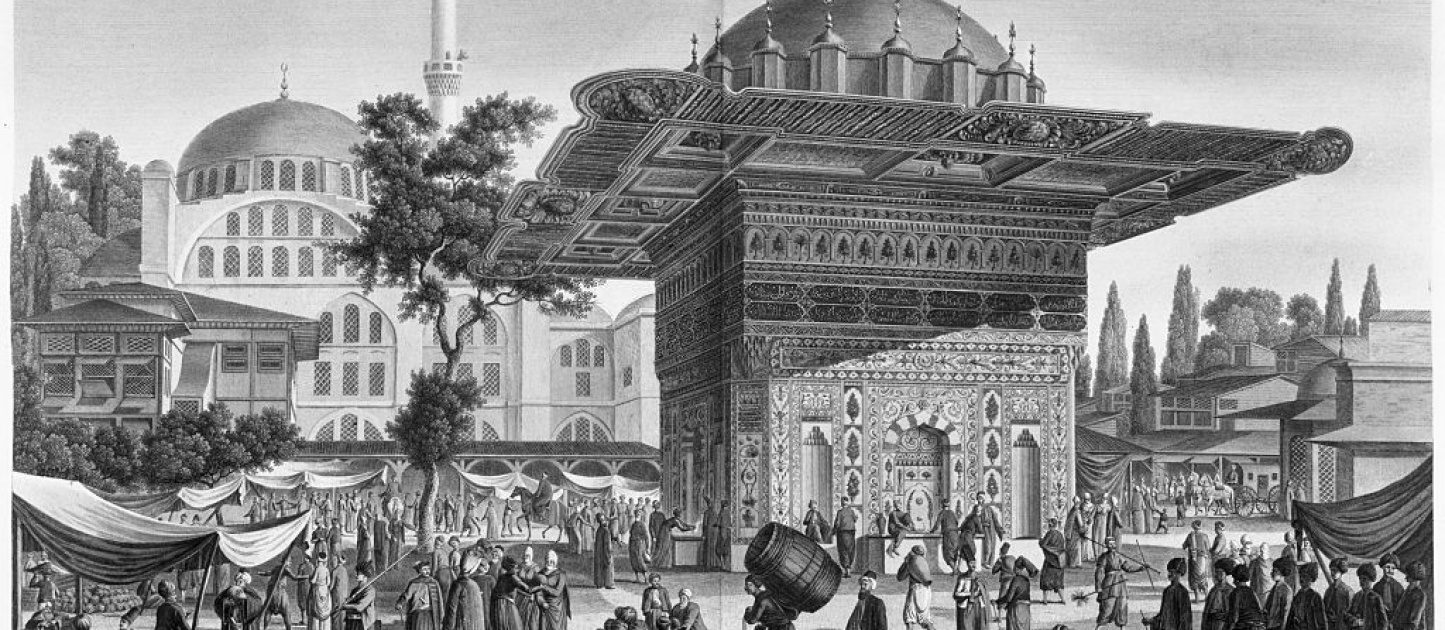
The period of the Empire known as the Tulip Period is a movement of art and architecture that took place between 1718-1730. During this period, architecture became a part of daily life and gained an important place in the social life of Ottoman society. This movement was based on many innovative ideas influenced by the Baroque and Rococo styles emerging in Western Europe. Tulip Period architecture is a unique style that emerged as Ottoman society adapted to the developing culture of Western Europe with a new self-confidence.
The architecture of the Tulip Period is characterized by palaces, mosques, fountains and mansions. The architecture of these buildings incorporates elements of traditional Ottoman architecture as well as Western European style. These buildings were often built with striking design and fine craftsmanship.
The architecture of the Tulip Period brought many innovations in the field of architecture. During this period, architecture became an engineering discipline rather than an art form for architects. During this period, architects gained more knowledge and experience in construction techniques in order to design beyond what had been done before. For this reason, the architecture of the Tulip Period is recognized as an important turning point in Ottoman society and the world of architecture.
Tulip Period architecture is famous for its ornate decorations and elaborate workmanship. The marble, stone and woodwork used on the facades of these buildings occupies a very important place in the history of architecture. Especially in fountains, the details designed with fine craftsmanship and colored ceramics reflect the traditional features of Ottoman architecture and are combined with Western European style ornaments.
The architecture of the Tulip Period reflects the architectural characteristics of Western Europe, moving away from the traditional features of Ottoman architecture. The buildings constructed during this period bear the characteristics of Baroque and Rococo style, such as straight and sharp lines, asymmetrical designs and proportioned shapes. This architectural style is the distinctive architectural structure of the Ottoman Empire.